
P. Kolar, M. S. Grbić, S. Hrabar, Sensors 19, 03064 (2019)
M. S. Grbić, JAP 125, 224501 (2019)
T. Cvitanić, M. Lukas, M. S. Grbić, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 90, 043903 (2019)
D. Pelc, P. Popčević, M. Požek, M. Greven, and N. Barišić, Sci. Adv. 5, eaau4538 (2019)
D. Pelc, H.-J. Grafe, G. D. Gu, and M. Požek, Phys. Rev. B 95, 054508 (2017).
R. Blinder et al. Phys. Rev. B 95, 020404(R) (2017).
D. Pelc, M. Vučković, H.-J. Grafe, S.-H. Baek, M. Požek, Nature Communications 7, 12775 (2016).
D. Pelc, M. Požek, V. Despoja and D. K. Sunko, New J. Phys. 17, 083033 (2015).
M. Došlić, D. Pelc and M. Požek, Rev. Sci. Instrum 85, 073905 (2014).
T. Cvitanić, D. Pelc, M. Požek, E. Amit, and A. Keren, Phys. Rev. B 90, 054508 (2014).
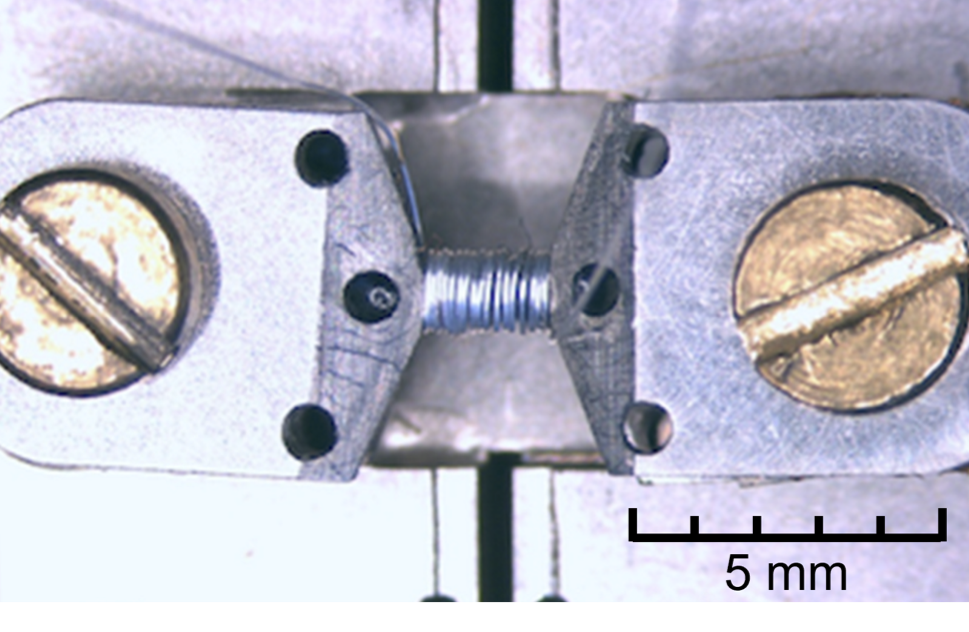 |
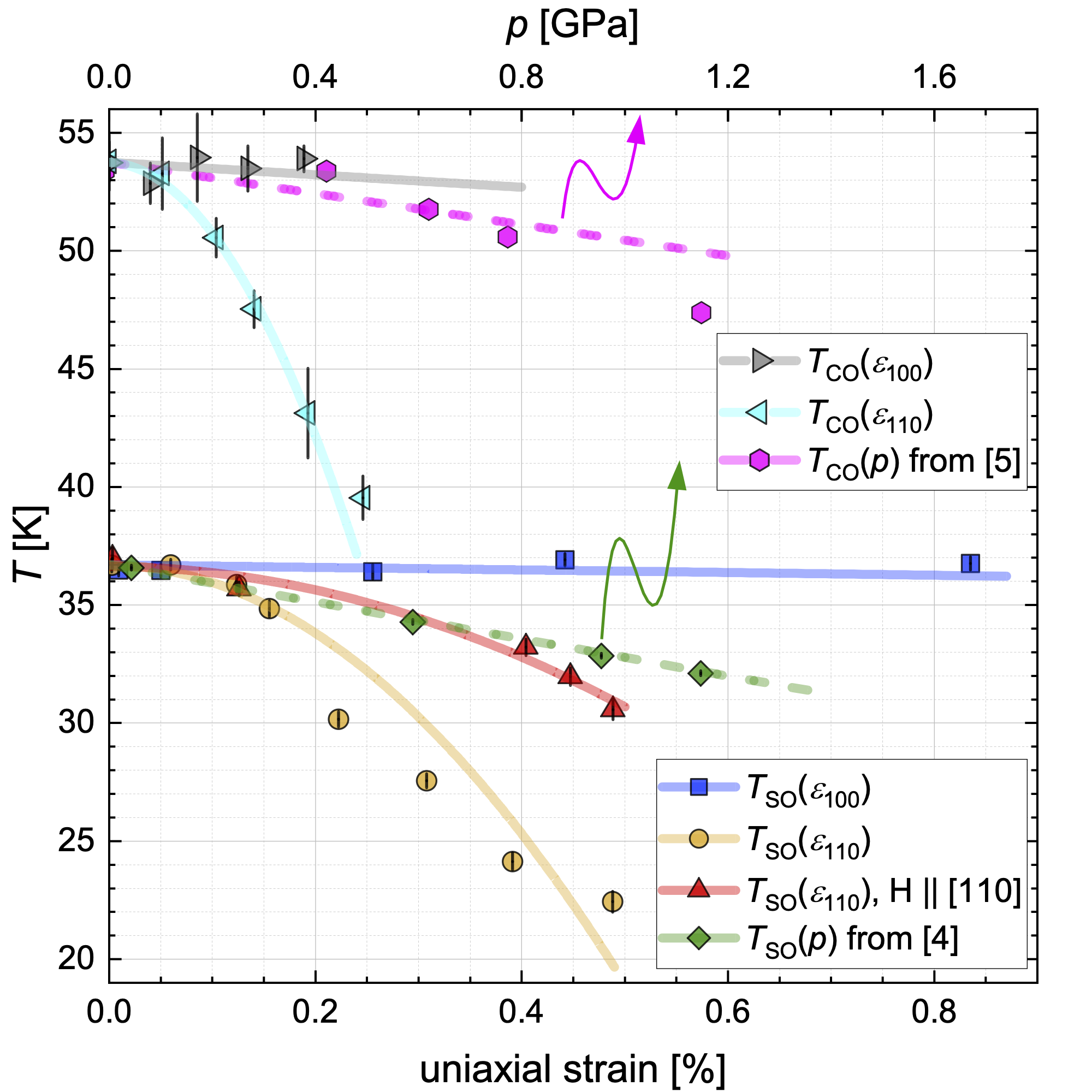
I. Jakovac, M. Požek and M.S. Grbić published a paper in Physical Review B where uniaxial stress was used to control the transition temperatures of the charge and spin "stripe phase" in the compound La1.875Ba0.125CuO4. The study was made using 139La NMR and 63Cu NQR. While in the unstrained state, a low-temperature tetragonal structure is formed below TLTT = 57 K, and the charge and spin transitions are at, respectively, TCO = 54 K and TSO = 37 K. We found that straining along the [110] crystallographic direction greatly suppresses TCO and TSO, although the TLTT is only slightly altered. In other words, straining along [110] causes a large divergence (≈ 21 K) between TCO and TLTT, indicating that these transitions are not strongly coupled. On the other hand, strain along [100] causes a (slight) suppression of the TLTT and has no effect on TCO and TSO. The magnetic field along [110] stabilizes the spin order: the suppression of the TSO by strain along [110] is weaker with the field along [110] than along [001]. |
To better understand these results, a Landau free energy model was developed, and we find that our results can be interpreted as the interplay of symmetry-breaking terms in the spin orientation.
Comparing our results with previous measurements under hydrostatic pressure p shows that the suppression of TCO and TSO can be fully explained by the effect of strain on the CuO2 planes.
The paper is available at the following link.
The research was carried out with the support of the Croatian Science Foundation (project IP-2018-01-2970), the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation (project 3.4-1022249-HRV-IP), the CeNIKS project co-financed by the Croatian Government and the European Regional Development Fund, Operational Programme Competitiveness and Cohesion (project KK.01.1.1.02.0013).

