
P. Kolar, M. S. Grbić, S. Hrabar, Sensors 19, 03064 (2019)
M. S. Grbić, JAP 125, 224501 (2019)
T. Cvitanić, M. Lukas, M. S. Grbić, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 90, 043903 (2019)
D. Pelc, P. Popčević, M. Požek, M. Greven, and N. Barišić, Sci. Adv. 5, eaau4538 (2019)
D. Pelc, H.-J. Grafe, G. D. Gu, and M. Požek, Phys. Rev. B 95, 054508 (2017).
R. Blinder et al. Phys. Rev. B 95, 020404(R) (2017).
D. Pelc, M. Vučković, H.-J. Grafe, S.-H. Baek, M. Požek, Nature Communications 7, 12775 (2016).
D. Pelc, M. Požek, V. Despoja and D. K. Sunko, New J. Phys. 17, 083033 (2015).
M. Došlić, D. Pelc and M. Požek, Rev. Sci. Instrum 85, 073905 (2014).
T. Cvitanić, D. Pelc, M. Požek, E. Amit, and A. Keren, Phys. Rev. B 90, 054508 (2014).
In the Soft matter magazine our group published a scientific paper titled 'Role of microscopic phase separation in gelation of aqueous gelatin solution', authored by Damjan Pelc, Mario Basletić and Miroslav Požek of the Physics Department together with Sanjin Marion from the Institue of Physics. The work shows a study of gelatine molecule dynamics in aqueous solution by a combination of techniques: circular dichroism spectroscopy and diffusion measurements using pulsed field gradient NMR.
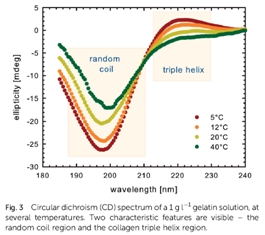 Although it has been known for a while that gelatine molecules get locally connected and form helical segments, the mechanism of gel formation has not been resolved even today. In the published paper [1] we have showed that emergent interactions between well defined helical segments play a key role by causing aggregation of molecules into larger clusters - threads - thus creating a gelatine network. This has been established by studying dynamical environment of molecules which are not a part of the network by two complementary methods: circular dichroism spectroscopy and diffusion NMR. The work on this problem has been started by Damjan Pelc and Sanjin Marion mentored by Mario Basletić during their project for the highly respected University of Zagreb’s Rector prize in 2010. Later on, they expanded their research to NMR. Experiments are a result of many years of effort in development of measurement techniques at the Physics Department, followed by several key innovations [2] which enabled highly precise determination of gelatine conductivity at low frequencies. Combining the conductivity measurements with NMR makes it possible to access different information on molecule dynamics: characteristic relaxation times and length scales, number of ‘free’ molecules etc., which gave the team the insight to the local structure of gelatine and show a clear evidence of microscopic phase separation, i.e. cluster formation.
Although it has been known for a while that gelatine molecules get locally connected and form helical segments, the mechanism of gel formation has not been resolved even today. In the published paper [1] we have showed that emergent interactions between well defined helical segments play a key role by causing aggregation of molecules into larger clusters - threads - thus creating a gelatine network. This has been established by studying dynamical environment of molecules which are not a part of the network by two complementary methods: circular dichroism spectroscopy and diffusion NMR. The work on this problem has been started by Damjan Pelc and Sanjin Marion mentored by Mario Basletić during their project for the highly respected University of Zagreb’s Rector prize in 2010. Later on, they expanded their research to NMR. Experiments are a result of many years of effort in development of measurement techniques at the Physics Department, followed by several key innovations [2] which enabled highly precise determination of gelatine conductivity at low frequencies. Combining the conductivity measurements with NMR makes it possible to access different information on molecule dynamics: characteristic relaxation times and length scales, number of ‘free’ molecules etc., which gave the team the insight to the local structure of gelatine and show a clear evidence of microscopic phase separation, i.e. cluster formation.
[1] D. Pelc, S. Marion, M. Požek, M. Basletić, Soft Matter 10, 348 (2014)
[2] D. Pelc, S. Marion, M. Basletić, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 82, 073907 (2011)